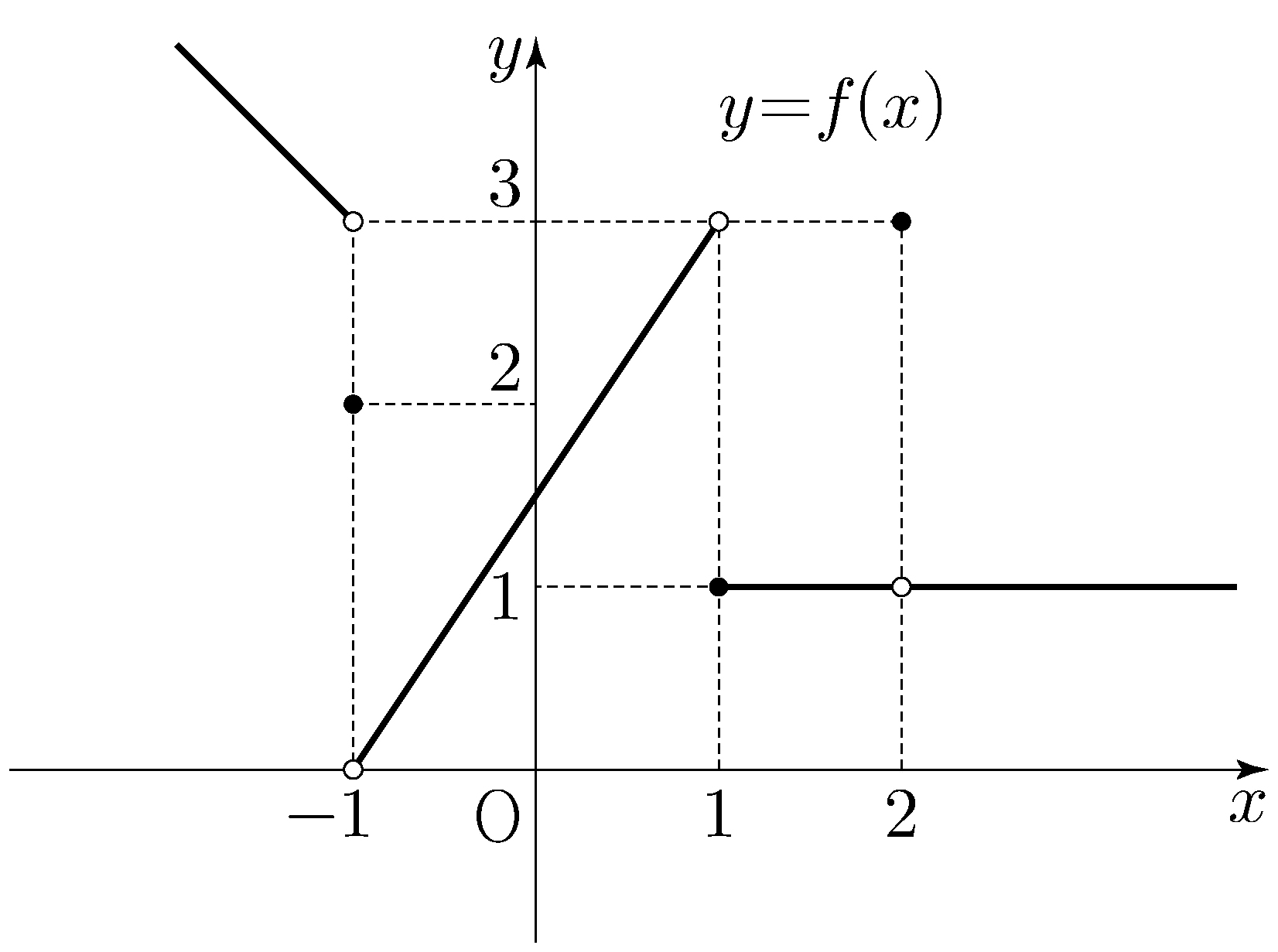
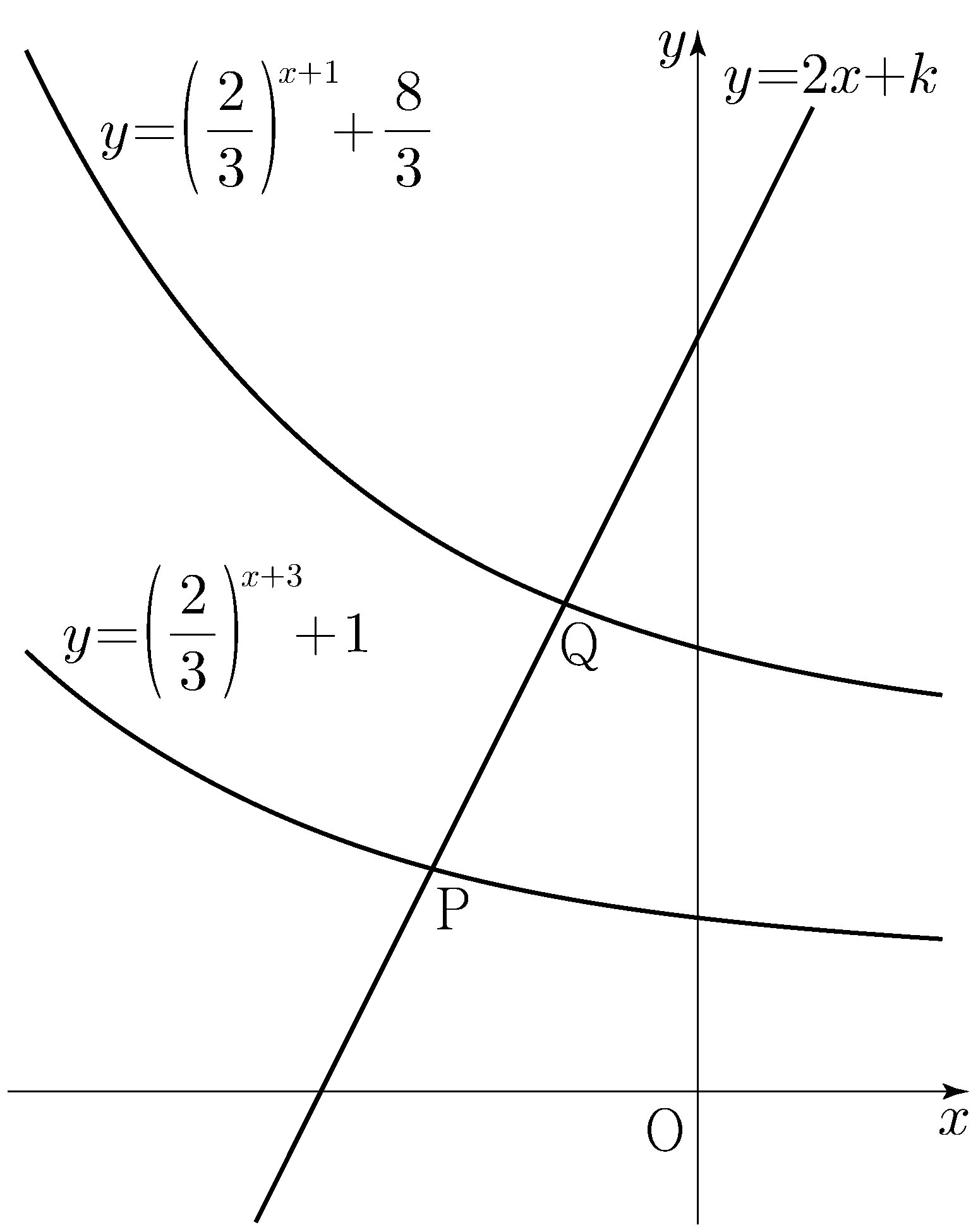
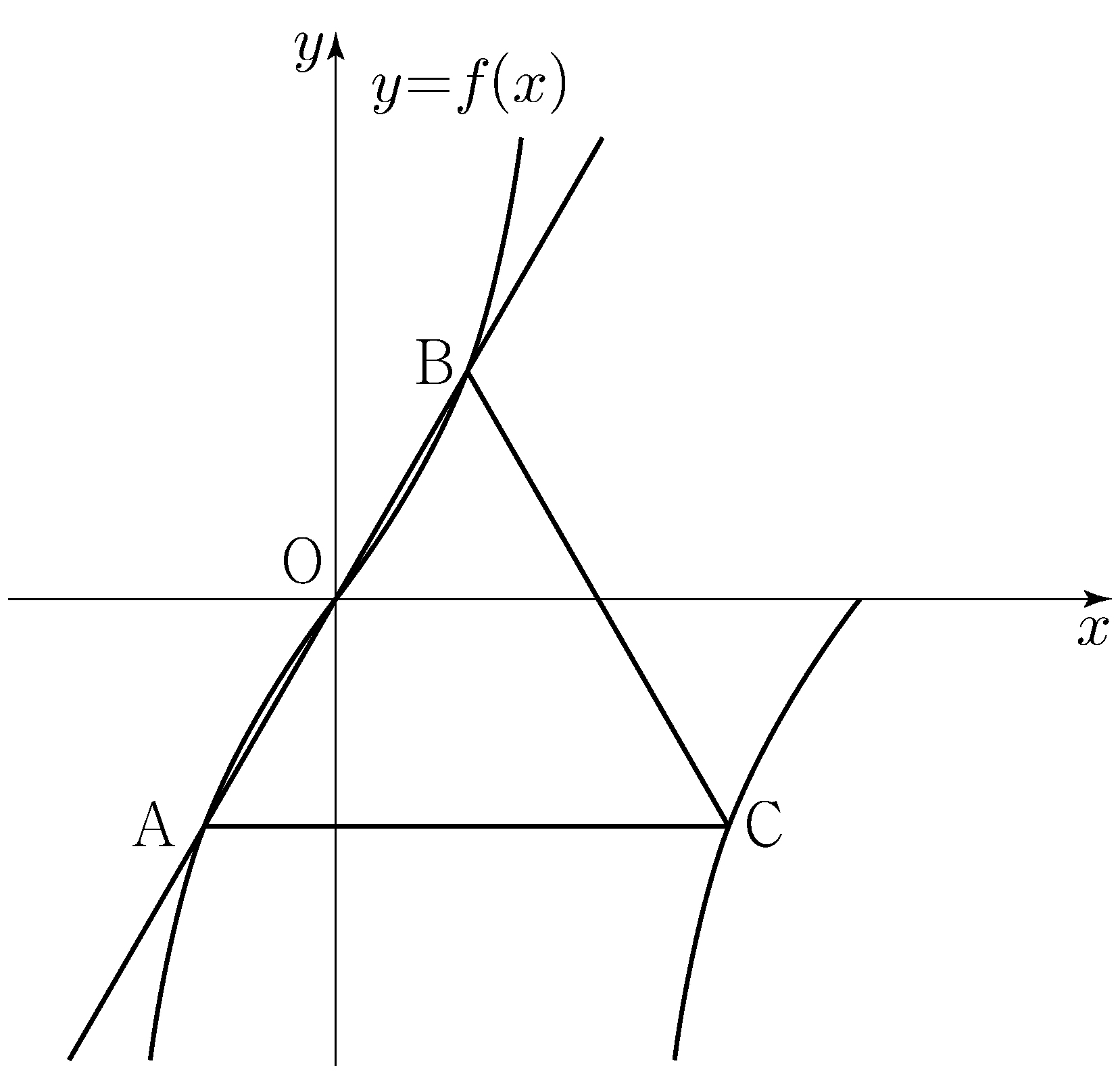
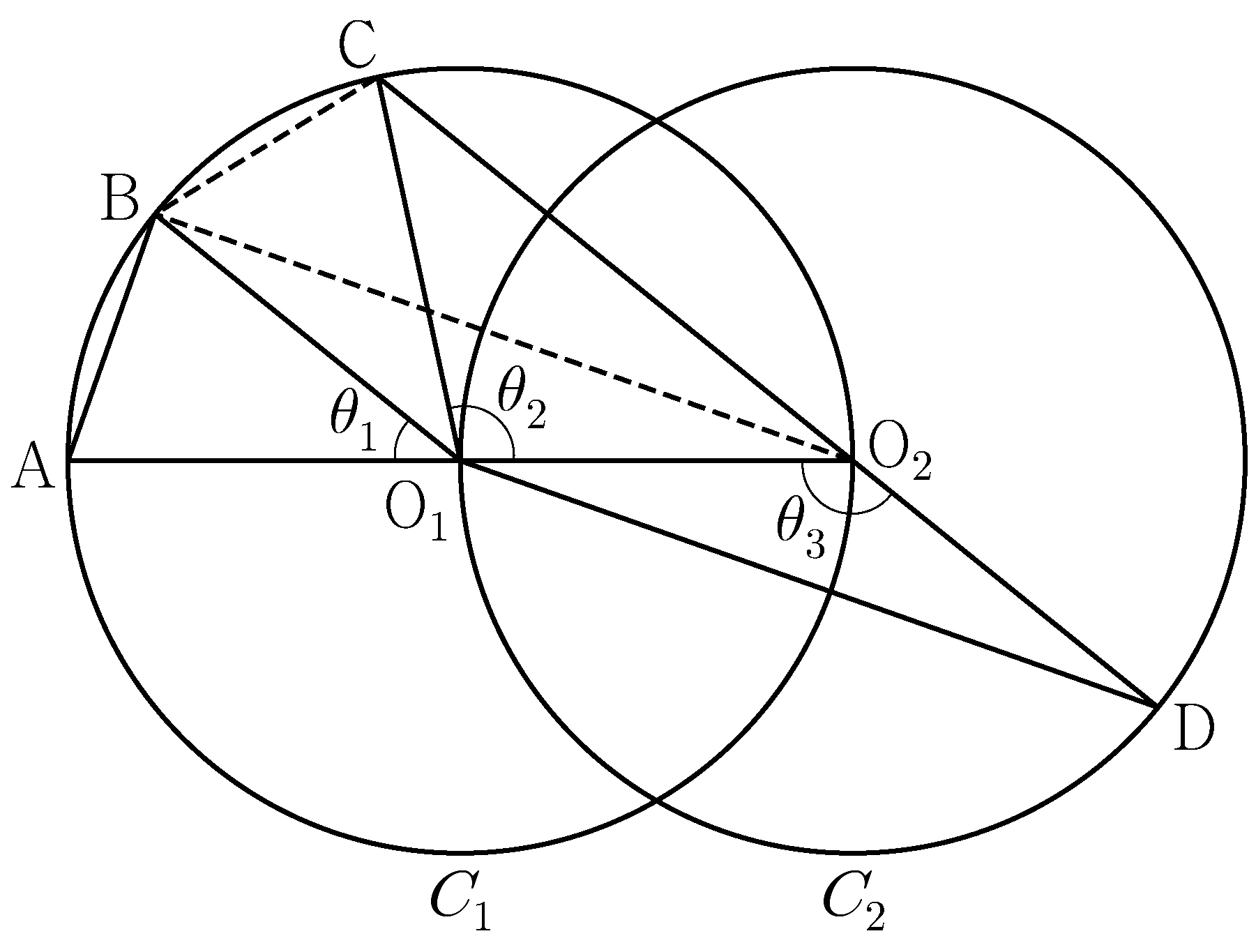
\(\angle\mathrm{CO_2O_1}+\angle\mathrm{O_1O_2D}=\pi\),
so \(\theta_3=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+\dfrac{\theta_2}{2}\).
\(\theta_3=\theta_1+\theta_2\), so \(2\theta_1+\theta_2\!=\!\pi\)
and \(\angle\mathrm{CO_1B}=\theta_1\).
Since \(\angle\mathrm{O_2O_1B}=\theta_1+\theta_2=\theta_3\),
triangles \(\mathrm{O_1O_2B}\) and \(\mathrm{O_1O_2B}\) are congruent.
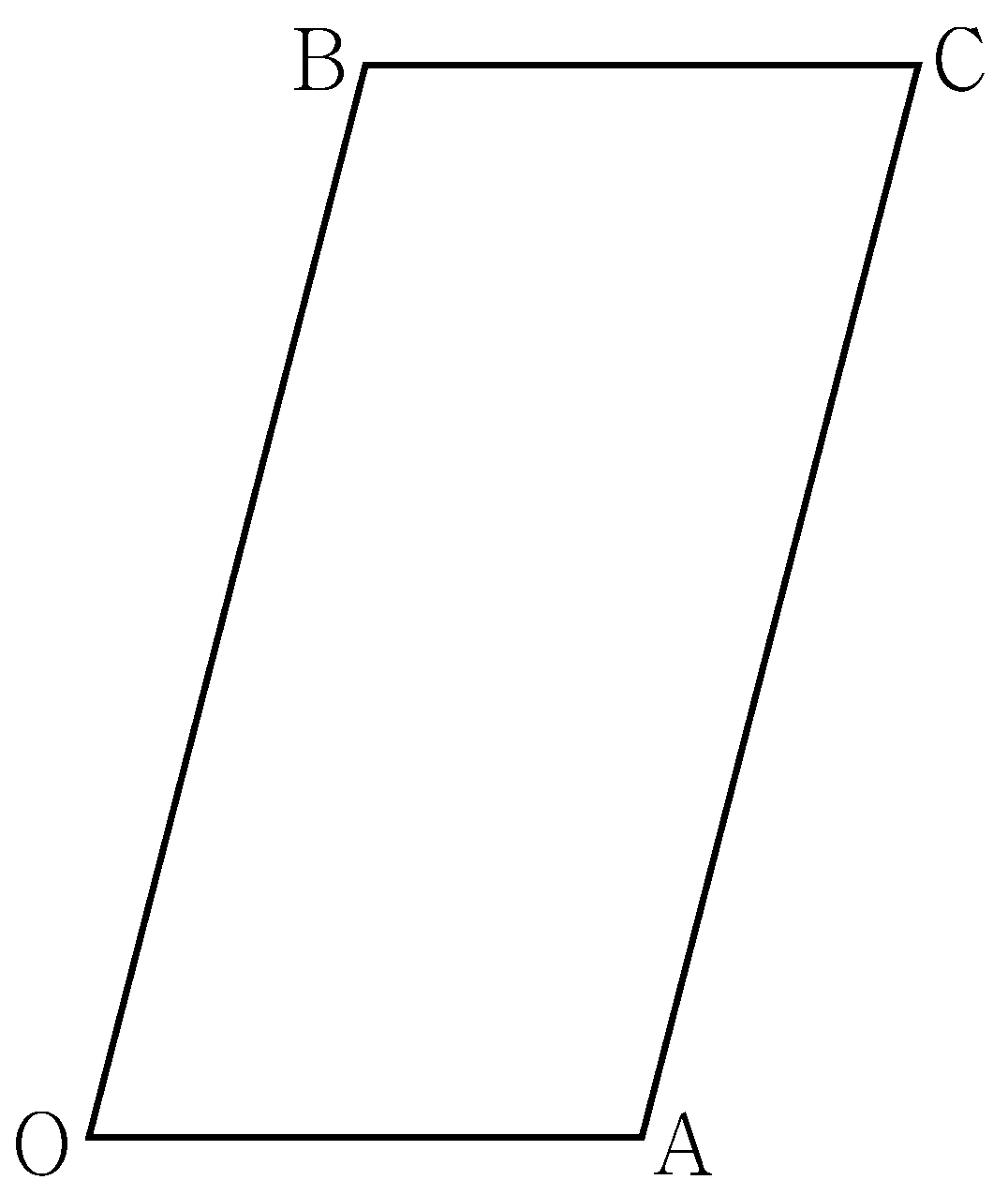
Suppose \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}=k\).
Then \(\overline{\mathrm{BO_2}}=\overline{\mathrm{O_1D}}=2\sqrt{2}k\),
so \(\overline{\mathrm{AO_2}}=\fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)}\).
\(\angle\mathrm{BO_2A}=\dfrac{\theta_1}{2}\), therefore
\(\cos\!\dfrac{\theta_1}{2}=\fbox{\(\;(\beta)\;\)}\).
In the triangle \(\mathrm{O_2BC}\),
\(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}=k, \overline{\mathrm{BO_2}}=2\sqrt{2}k\), and
\(\angle\mathrm{CO_2B}=\dfrac{\theta_1}{2}\),
so \(\overline{\mathrm{O_2C}}=\fbox{\(\;(\gamma)\;\)}\)
by the law of cosines.
\(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}=\overline{\mathrm{O_2D}}+\overline{\mathrm{O_2C}}
=\overline{\mathrm{O_1O_2}}+\overline{\mathrm{O_2C}}\),
therefore
\(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}:\overline{\mathrm{CD}}=
k:\Big(\dfrac{\fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)}}{2}+\fbox{\(\;(\gamma)\;\)}\,\Big)\).