\(a_{n+1} = \dfrac{S_n^2}{S_{n-1}} + (2n-1)S_n \quad (n\geq 2)\)
where \(S_n= \displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{n}a_k\).
The following is a process computing the general term \(a_n\).
Since \(a_{n+1}=S_{n+1}-S_n\), we have
\(S_{n+1} = \dfrac{S_n^2}{S_{n-1}} + 2nS_n \quad (n\geq 2)\).
Dividing both sides with \(S_n\), we have
\(\dfrac{S_{n+1}}{S_n} = \dfrac{S_n}{S_{n-1}}+2n\).
Let \(b_n = \dfrac{S_{n+1}}{S_n}\).
Then \(b_1=2\), and
\(b_n=b_{n-1}+2n \quad (n\geq 2)\).
The general term of the sequence \(\{b_n\}\) is
\(b_n = \fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)} \times (n+1) \quad (n\geq 1)\),
therefore
\(S_n =\fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)} \times \{(n-1)!\}^2 \quad (n\geq 1)\).
Therefore \(a_1=1\), and
\(\begin{align}
a_n &= S_n-S_{n-1} \\
&= \fbox{\(\;(\beta)\;\)} \times \{(n-2)!\}^2
\end{align}\)
for \(n\geq 2\).

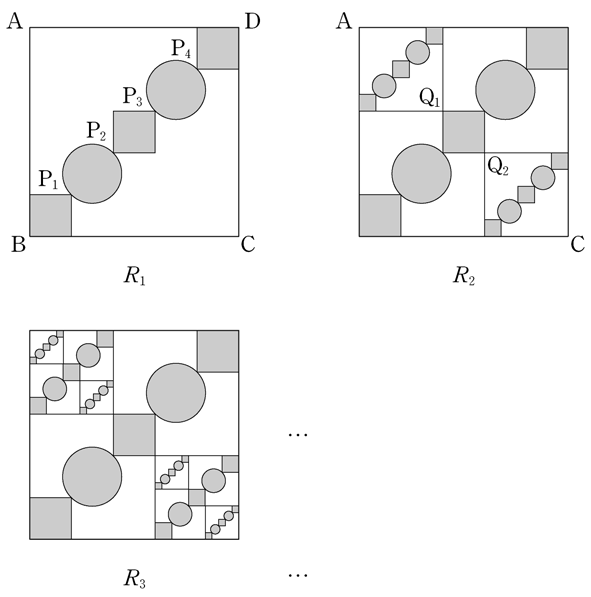
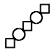 shape.
shape.
 shapes,
by applying the method used to obtain figure \(R_1\)
to the newly drawn two squares respectively.
shapes,
by applying the method used to obtain figure \(R_1\)
to the newly drawn two squares respectively.
 shapes
on two squares with line segments \(\mathrm{AQ_1}\)
and \(\mathrm{CQ_2}\) as a diagonal respectively,
with the method used to obtain figure \(R_2\) from figure \(R_1\).
shapes
on two squares with line segments \(\mathrm{AQ_1}\)
and \(\mathrm{CQ_2}\) as a diagonal respectively,
with the method used to obtain figure \(R_2\) from figure \(R_1\).