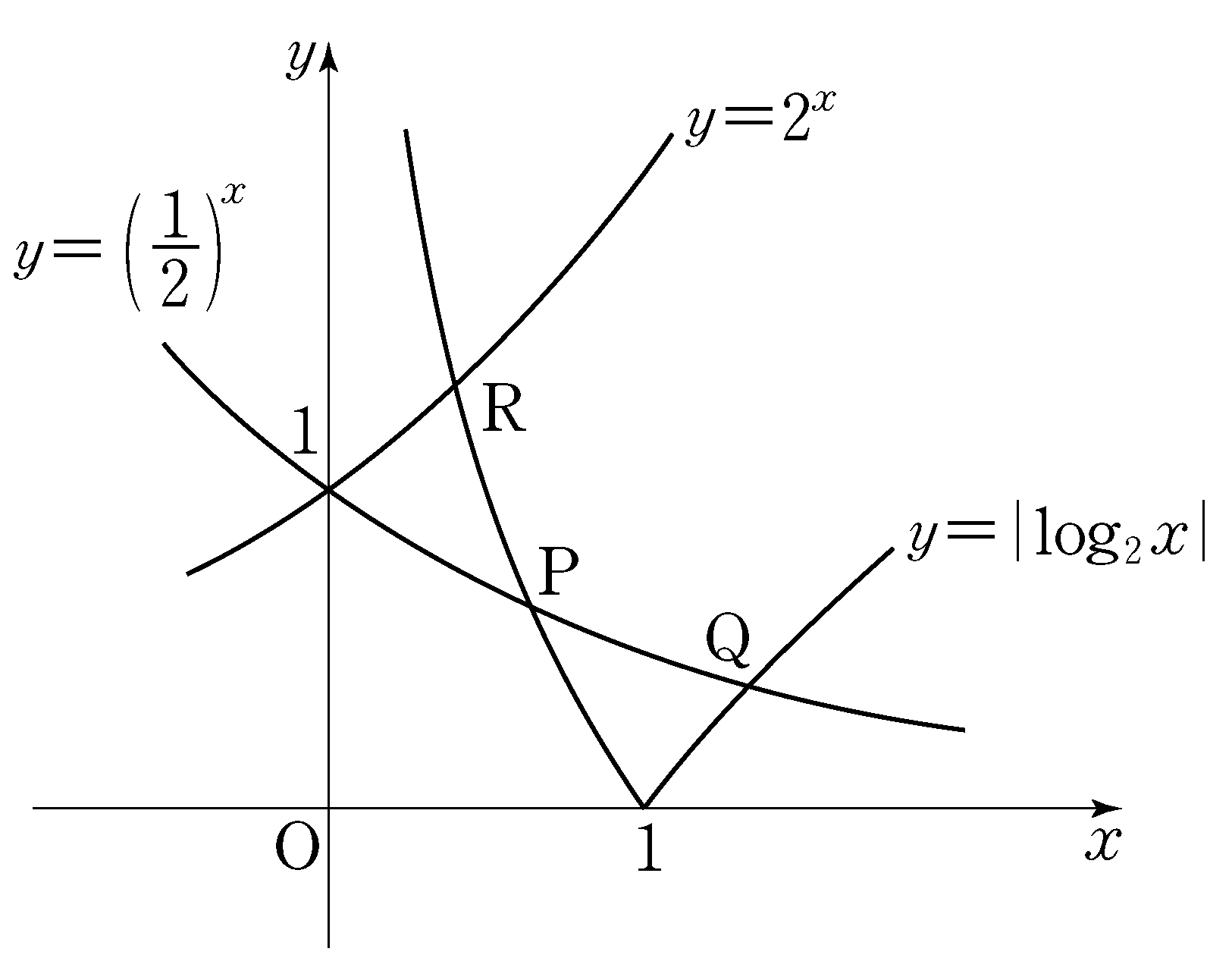
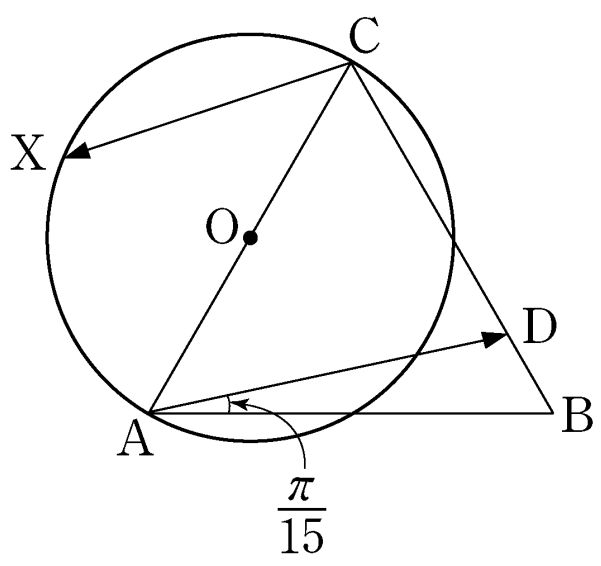
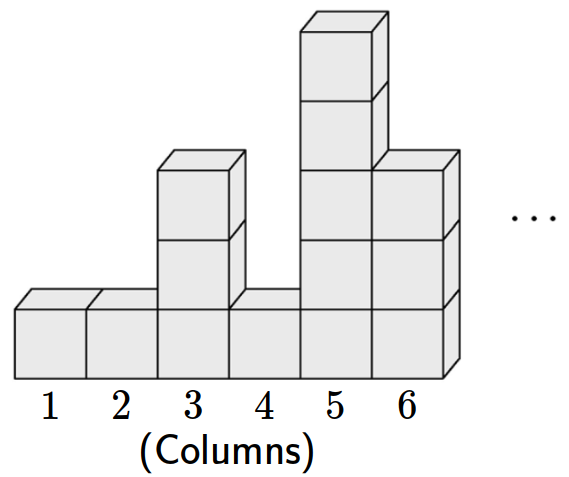
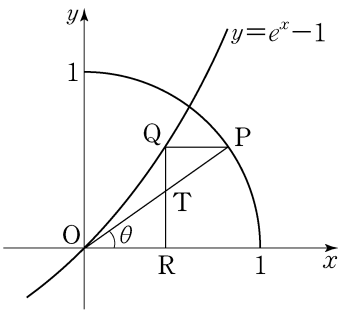
- \(5\)
- \(4\)
- \(3\)
- \(2\)
- \(1\)
Mathematics (Type Ga)
|
Score
Category
|
Score \(\mathrm{A}\) | Score \(\mathrm{B}\) | Score \(\mathrm{C}\) |
| Audience vote | \(40\) | \(30\) | \(20\) |
| Judge panel | \(50\) | \(40\) | \(30\) |
- \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
- \(\dfrac{11}{36}\)
- \(\dfrac{5}{18}\)
- \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{2}{9}\)
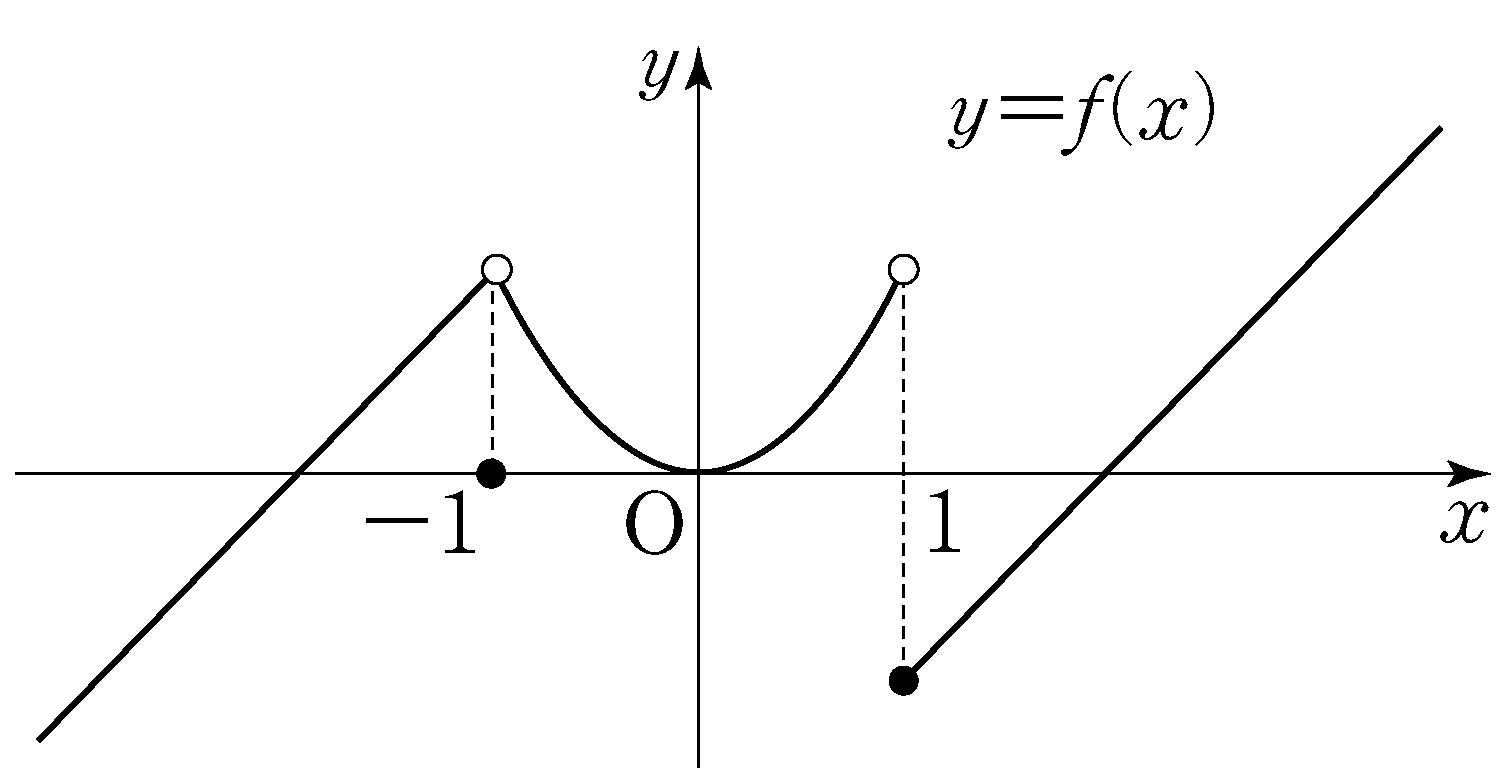
\(f(x)=\begin{cases}
x+2 & \; (x<-1)\\
0 & \; (x=-1)\\
x^2 & \; (-1<x<1)\\
x-2 & \; (x\geq 1).
\end{cases}\)
Which option only contains every correct statement in the <List>?
[3 points]
- \(\displaystyle\lim_{x\to 1+0}\{f(x)+f(-x)\}=0\)
- The function \(f(x)-|f(x)|\) has a discontinuity at exactly \(1\) point.
- There is no constant \(a\) for which the function \(f(x)f(x-a)\) is continuous on the set of all real numbers.
- a
- a, b
- a, c
- b, c
- a, b, c