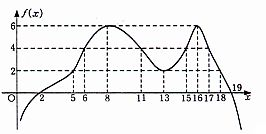
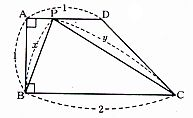
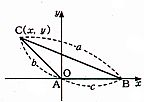
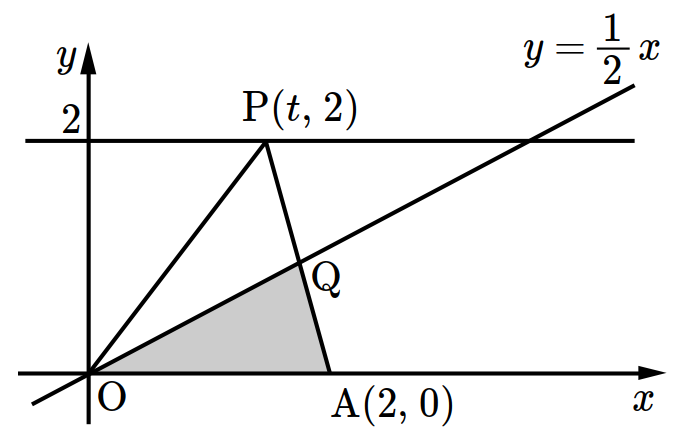
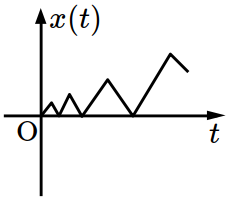- \(1\)
- \(3\)
- \(4\)
- \(8\)
- \(11\)
Mathematics·Studies (I)
Nat. Sciences
- \(A\cup B=B\)
- \(A\cap B=A\)
- \((A\cap B)^c=B^c\)
- \(B^c \subseteq A^c\)
- \(A-B=\varnothing\)
\((h \circ g \circ f)(x)=h(x)\)
for all functions \(h(x)\).
What is the value of \(g(3)\)?
(※ \(f(x), g(x)\) and \(h(x)\) are functions from \(R\) to \(R\), where \(R\) is the set of all real numbers.) [1 point]
- \(-2\)
- \(-1\)
- \(0\)
- \(1\)
- \(2\)
- \(34\)
- \(33\)
- \(32\)
- \(31\)
- \(30\)
\(\dfrac{1}{(x-1)(x-2)\cdots(x-10)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a_1}{x-1} + \dfrac{a_2}{x-2} + \cdots + \dfrac{a_{10}}{x-10}\)
is satisfied for all real numbers \(x\) that does not make the denominator \(0\).
What is the value of \(a_1+a_2+\cdots+a_{10}\)?
[1.5 points]
- \(0\)
- \(-1\)
- \(1\)
- \(-10\)
- \(10\)